本文基于IEEE Std 802.3-2022 PCS 章节,介绍几种66b同步方法,处理位宽包括64bit数据到32bit数据,并给出一些优化方案。
整个简化流程可以表示为:
64bit输入数据->增加同步头->转换成64bit位宽数据-----> PMA tx ----->PMA rx ---->66b同步->去同步头->64bit数据
在上述流程中,没有包括加解扰,也没有包括FEC编解码及帧同步,这些内容后续再补充。PMA属于模拟部分,也不包括。
1.整体框架
假设发送模块输入信号分别为 i_control, i_data, i_frame_first, i_valid。这三个信号分别表示当前数据包含控制符(影响同步头),输入数据,起始帧指示(32拍64bit信号作为一帧),数据有效指示信号。模块输出数据为o_data,o_valid,此时输出数据为纯数据流。
解释一下为什么需要i_frame_first 这个信号,由于32拍数据会插入64bit同步头,说明下一拍输入数据valid数据要保持低电平并且输出缓存下来的第33个64bit数据,所以是33拍数据一个循环。如果没有这个i_frame_first 指示信号根据33拍的周期重复校准,一旦内部计数器有扰动就再也无法和输入数据对齐了。这个问题我们可以在后续代码中查看。
首先来构造一下激励:
module top();
reg clk = 0;
reg rst_n = 0;
always #5 clk = ~clk;
reg [6:0] cnt33 = 'd0;
reg data_vld;
reg first_dat;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(rst_n == 1'd0)begin
cnt33 <= 'd0;
data_vld <= 'd0;
first_dat <= 'd1;
end
else if(cnt33 == 'd32)begin
cnt33 <= 'd0;
data_vld <= 'd0;
first_dat <= 'd0;
end
else begin
data_vld <= 'd1;
cnt33 <= cnt33 + 'd1;
first_dat <= cnt33 == 'd0;
end
end
initial begin
#50;
rst_n = 1;
#5000;
$finish;
end
initial begin
$fsdbDumpfile("top.fsdb");
$fsdbDumpvars(0,top);
$fsdbDumpMDA();
end
endmodule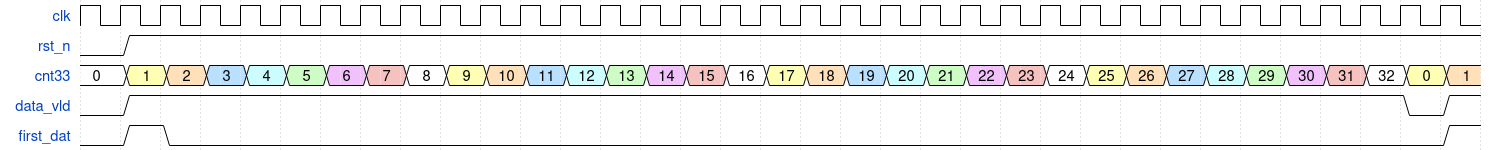
/*
# ------------------------------------
# File: /home/ssy/Code/hdl/MAC/pcs_66b_enc.v
# Project: /home/ssy/Code/hdl/MAC
# Created Date: Wednesday, December 17th 2025, 11:33:00 pm
# Author: Shirainbown
# -----
# Module: pcs_66b_enc.v
# -----
# Description:
# -----
# Copyright (c) 2025 Non Inc.
# ------------------------------------
*/
module pcs_66b_enc (
input clk,
input rst_n,
// Input interface (frame-based, 64-bit)
input [63:0] i_data,
input i_control,
input i_frame_first,
input i_valid,
// Output interface (pure 64-bit data stream)
output reg [63:0] o_data,
output reg o_valid
);
// ==============================
// 1. 64B/66B Encoder
// ==============================
localparam [1:0] SYNC_DATA = 2'b10;
localparam [1:0] SYNC_CONTROL = 2'b01;
wire [65:0] encoded_66b; // [65:64] = sync header
reg enc_valid;
assign encoded_66b = i_control ? {SYNC_CONTROL, i_data}: {SYNC_DATA, i_data};
// Register encoder output (1-cycle latency)
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if (!rst_n) begin
enc_valid <= 1'b0;
end else begin
enc_valid <= i_valid;
end
end
// ==============================
// 2. Frame Counter (for 32-block frame)
// ==============================
reg [6:0] frame_cnt; // 0 to 31
reg in_frame;
reg insert_gap; // after frame ends, insert 1-cycle gap
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if (!rst_n) begin
frame_cnt <= 7'd0;
end
else begin
if (i_valid) begin
frame_cnt <= i_frame_first == 1'd1 ? 7'd0 : frame_cnt + 1;
end else begin
frame_cnt <= frame_cnt>= 7'd32 ? 7'd0 :frame_cnt==7'd31 ? frame_cnt + 1 :frame_cnt;
end
end
end
// ==============================
// 3. Gearbox: 66b -> 64b
// Use a shift register to accumulate bits
// ==============================
reg [129:0] bit_buffer; // >= 66+64 = 130 bits
reg [7:0] buffer_bits; // number of valid bits in buffer
// Push 66b into buffer when valid
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if (!rst_n ) begin
bit_buffer <= 130'd0;
buffer_bits <= 8'd0;
end
else begin
if (i_valid) begin
bit_buffer <= {bit_buffer[63:0], encoded_66b};
buffer_bits <= i_frame_first ==1'd1 ? 8'd66 : buffer_bits - 8'd2;
end
end
end
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if (!rst_n) begin
o_data <= 64'd0;
o_valid <= 1'b0;
end else begin
if (buffer_bits >= 8'd64 || (buffer_bits > 8'd0 && enc_valid == 1'd1 ) ) begin
o_data <= bit_buffer[frame_cnt*2+65-:64];
o_valid <= 1'b1;
end else begin
o_valid <= frame_cnt == 7'd32 ? 1'd1:1'b0;
o_data <= frame_cnt == 7'd32 ? bit_buffer[63:0]: 64'd0;
end
end
end
endmodulemodule pcs_66b_dec (
input clk,
input rst_n,
// Input: pure 64-bit data stream (from descrambler)
input [63:0] i_data,
input i_valid, // usually always 1 in continuous mode
// Output: reconstructed frame interface
output reg [63:0] o_data,
output reg o_control,
output reg o_frame_first,
output reg o_valid
);
localparam [1:0] SYNC_DATA = 2'b10;
localparam [1:0] SYNC_CONTROL = 2'b01;
localparam LOCK_INIT = 3'd0;
localparam RESET_CNT = 3'd1;
localparam TEST_SH = 3'd2;
localparam 64_GOOD = 3'd4;
localparam SLIP = 3'd5;
wire [127:0] bit_buffer;
reg [63:0] i_data_1d;
reg [2:0] cur_state;
reg [2:0] next_state;
assign bit_buffer = {i_data_1d,i_data_1d};
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if (!rst_n) begin
i_data_1d <= 64'd0;
end
else begin
i_data_1d <= i_valid == 1'd1 ? i_data: i_data_1d;
end
end
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if (!rst_n) begin
cur_state <= LOCK_INIT;
end
else begin
cur_state <= next_state;
end
end
reg [6:0] good_count; // count of consecutive good SH
reg [4:0] bad_count; // count of invalid SH
reg [6:0] slip_cnt;
reg [0:0] valid_1d;
reg locked;
// Sync header extraction
wire [1:0] sync_hdr = bit_buffer[127-slip_cnt-:2];
wire is_valid_sh = (sync_hdr == 2'b01) || (sync_hdr == 2'b10);
wire is_control_block = (sync_hdr == 2'b01);
wire is_data_block = (sync_hdr == 2'b10);
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if (!rst_n) begin
valid_1d <= 1'b0;
end
else begin
valid_1d <= i_valid;
end
end
// State transition logic
always @(*) begin
case (cur_state)
LOCK_INIT: begin
next_sync_state = RESET_CNT;
end
RESET_CNT: begin
if (valid_1d) begin
if (is_valid_sh) begin
next_state = TEST_SH;
end
// else stay in SEARC
end
end
TEST_SH: begin
if(valid_1d)begin
if(good_count >= 7'd64 && bad_count == 5'd0 )begin
next_state = 64_GOOD;
end else if(good_count >= 7'd64 && bad_count < 5'd16)begin
next_state = locked == 1'd1 ? 64_GOOD : SLIP;
end
else if(bad_count >= 5'd16) next_state = SLIP;
end
end
64_GOOD: begin
next_state = RESET_CNT;
end
SLIP: begin
next_state = RESET_CNT;
end
default: next_state = LOCK_INIT;
endcase
end
reg rx_block_lock;
// Counters and lock flag
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if (!rst_n) begin
sh_cnt <= 6'd0;
invalid_sh_cnt <= 5'd0;
locked <= 1'b0;
end else begin
case (cur_state)
LOCK_INIT: begin
sh_cnt <= 6'd0;
invalid_sh_cnt <= 5'd0;
locked <= 1'b0;
end
RESET_CNT: begin
sh_cnt <= 6'd0;
invalid_sh_cnt <= 5'd0;
end
TEST_SH: begin
if (valid_1d) begin
if (is_valid_sh) begin
good_count <= good_count + 1;
bad_count <= 5'd0; // reset bad count on good SH
end else begin
good_count <= good_count ;
bad_count <= bad_count + 1;
end
end
end
64_GOOD: begin
rx_block_lock <= 1'b1;
end
SLIP: begin
rx_block_lock <= 1'b0;
slip_cnt <= slip_cnt +1;
end
endcase
end
end
// ==================================================
// 3. Output Generation (only when locked and valid block)
// ==================================================
// Detect Start-of-Frame (/S/)
// Assume control block with all bytes = 0xFB is /S/
// In practice, check first byte or specific pattern
wire is_start_of_frame = is_control_block && (raw_66b[63:56] == 8'hFB);
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if (!rst_n) begin
o_data <= 64'd0;
o_control <= 1'b0;
o_frame_first <= 1'b0;
o_valid <= 1'b0;
end else begin
if (rx_block_lock && block_valid && is_valid_sh) begin
o_data <= raw_66b[63:0];
o_control <= is_control_block;
o_frame_first <= is_start_of_frame;
o_valid <= 1'b1;
end else begin
o_valid <= 1'b0;
// Keep other outputs stable or zero
end
end
end
endmodule

评论